 Are you in the market for a new home? Have you considered the allure of a fixer-upper? While the idea of purchasing a home that needs a bit of TLC might seem daunting at first, numerous benefits come with this type of investment. We will plunge into the exciting world of fixer-uppers and uncover why they might just be the perfect choice for you.
Are you in the market for a new home? Have you considered the allure of a fixer-upper? While the idea of purchasing a home that needs a bit of TLC might seem daunting at first, numerous benefits come with this type of investment. We will plunge into the exciting world of fixer-uppers and uncover why they might just be the perfect choice for you.
Cost-Effectiveness: One of the most significant advantages of buying a fixer-upper is the potential cost savings. Typically, these homes are priced lower than move-in-ready properties, allowing you to purchase a larger or better-located home for the same budget. Additionally, you have the opportunity to increase the home’s value through renovations, ultimately yielding a higher return on investment.
Personalization: With a fixer-upper, you have the chance to create your dream home from the ground up. Instead of settling for someone else’s design choices, you can tailor the renovations to fit your style and preferences. Whether you’re envisioning an open-concept living space, a gourmet kitchen, or a luxurious master suite, the possibilities are endless when you’re starting with a blank canvas.
Building Equity: Renovating a fixer-upper allows you to build equity in your home right from the start. As you invest in upgrades and improvements, you’re increasing the property’s value, which can translate into substantial gains over time. Whether you decide to sell in the future or simply enjoy the added equity, it’s a win-win situation for your financial portfolio.
Learning Experience: Buying a fixer-upper is not just a financial investment; it’s also an opportunity for personal growth and learning. From tackling DIY projects to working with contractors, you’ll gain valuable skills and knowledge along the way. Plus, there’s a sense of pride that comes with knowing you’ve played a hands-on role in transforming your living space.
Community Revitalization: By investing in a fixer-upper, you’re not only improving your own home but also contributing to the revitalization of your community. Renovating an older or neglected property can have a positive ripple effect, inspiring neighbors to invest in their homes and enhancing the overall appeal of the area.
Flexibility: Unlike purchasing a move-in ready home, buying a fixer-upper allows you to take your time with renovations and upgrades. You can prioritize projects based on your budget and timeline, making it easier to manage the financial aspect of homeownership. Plus, you have the freedom to live in the home during renovations or tackle projects gradually as time and resources allow.
While buying a fixer-upper may require a bit more effort upfront, the benefits far outweigh the challenges. From cost savings and personalization to equity building and community impact, investing in a fixer-upper is a decision that can positively impact your life in more ways than one. So why wait? Take the plunge and uncover the hidden treasures awaiting you in the world of fixer-uppers. Your dream home might be closer than you think!

 Expert insights from Roger Young and the Peyton Mortgage Team in Houston, TX.
Expert insights from Roger Young and the Peyton Mortgage Team in Houston, TX.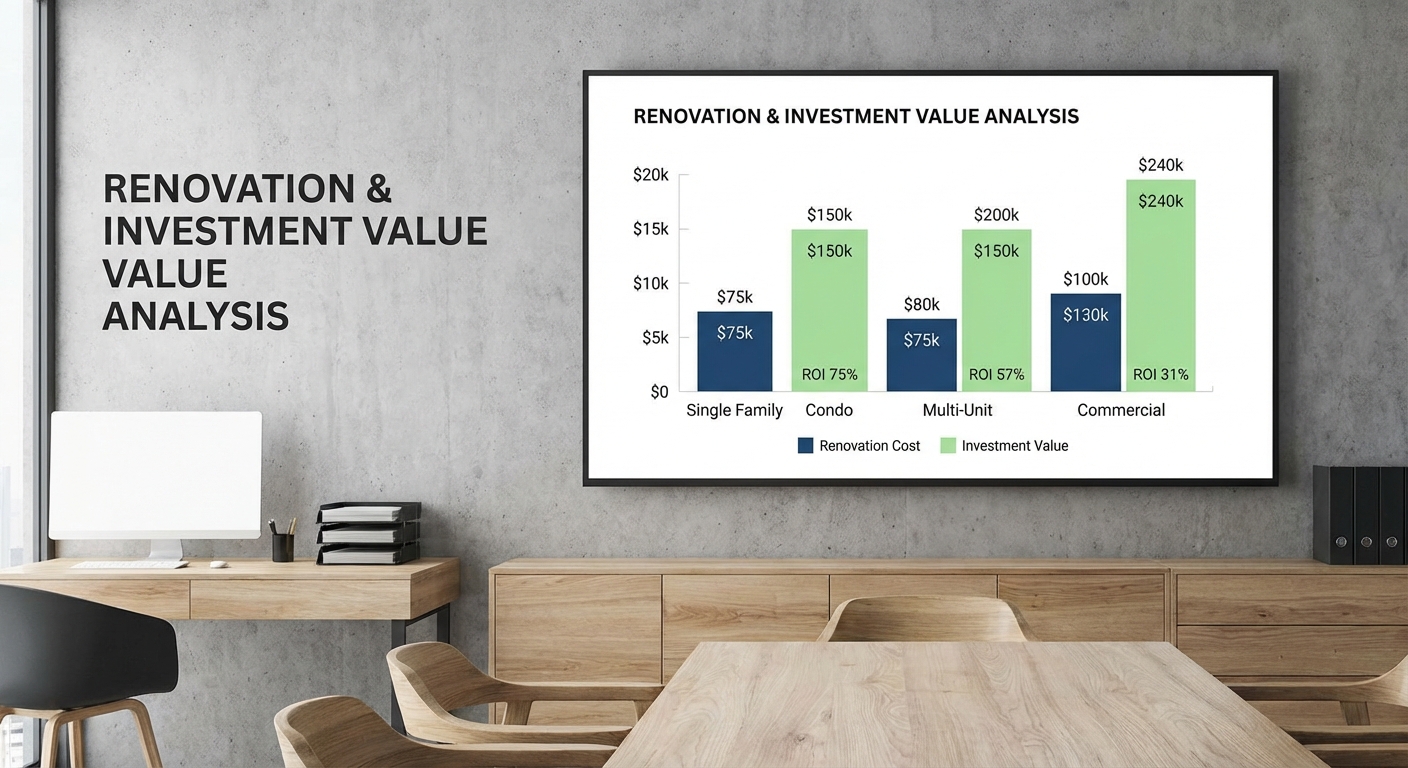 If you are considering this, visit our
If you are considering this, visit our  Inflation reports have shown their cards, and they have come in line with expectations. These newer reports rely on less data from sources overall, which is why the PCE Index remains the Federal Reserve’s preferred inflation indicator—and that distinction is even more relevant now.
Inflation reports have shown their cards, and they have come in line with expectations. These newer reports rely on less data from sources overall, which is why the PCE Index remains the Federal Reserve’s preferred inflation indicator—and that distinction is even more relevant now.